SQL Tutorial : Creating a Table and Inserting data ( MySQL & HSQLDB )
In this tutorial, we will learn how to create a database table and insert data into it, The example we will consider is a simple phone book to store names, last names, ages, email and phone numbers for people.
What is SQL?
- SQL stands for Structured Query Language
- SQL lets you access and manipulate databases
- SQL is an ANSI (American National Standards Institute) standard
What Can SQL do?
- SQL can execute queries against a database
- SQL can retrieve data from a database
- SQL can insert records in a database
- SQL can update records in a database
- SQL can delete records from a database
- SQL can create new databases
- SQL can create new tables in a database
- SQL can create stored procedures in a database
- SQL can create views in a database
- SQL can set permissions on tables, procedures, and views
1) We need to download the DBMS ( HSQLDB ): [a software that eases and facilitates accessing, managing and controlling the database]
[info]You need to download the DBMS : HSQLDB from here [/info]
2) Double click on the downloaded file ( hsqldb.jar ) to run it.
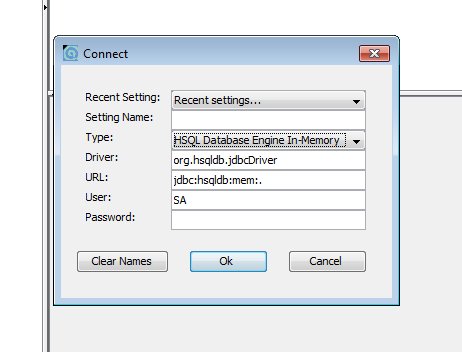
3) Click [OK]
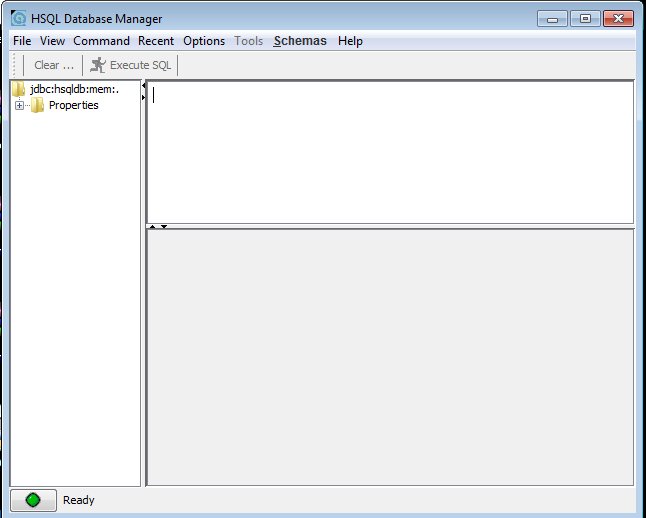
4) You will get the main screen for the DBMS, As shown below : The top section of the screen is for writing SQL queries: the bottom section for showing the results.
5) Type in this command into the top SQL section, Click [Execute SQL]
SET DATABASE SQL SYNTAX MYS TRUE
This command will allow HSQLDB to accept the synatx of MySQL so that we can use auto_increment, text …..
6) Click [Clear ] to clear the SQL commands.
7) Type in the following SQL command to create the table, Click [Execute SQL]
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS contacts (
contacts_id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(45) NOT NULL ,
lastname varchar(45) NOT NULL,
email text ,
age int,
phone varchar(45) NOT NULL
)
auto_increment : allows a unique number to be generated when a new record is inserted into a table.
primary key : constraint uniquely identifies each record in a database table. Primary keys must contain unique values. A primary key column cannot contain NULL values.
NOT NULL : The NOT NULL constraint enforces a column to NOT accept NULL values.
Basic Types for MySQL are : varchar, text,int, bigint, date, time, blob,,,,
8) To insert data into the table: let’s use :
INSERT INTO contacts
(name,lastname,email,age,phone)
VALUES
('Jerry', 'Yang','jerry@yahoo.com','41','0911')
Note that because contacts_id is set to auto_increment, we don’t need to specify it.
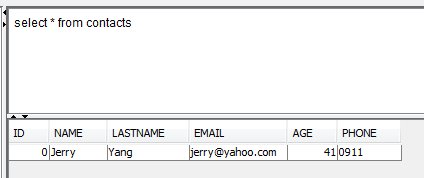
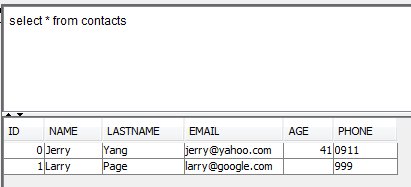
9) Let’s see what’s inside the table:
select * from contacts
We see that Jerry, was assigned the ID=0,
Let’s insert another data now:
INSERT INTO contacts
(name,lastname,email,phone)
VALUES
('Larry', 'Page','larry@google.com','999')
We don’t need to specify the age for Larry here. Let’s view the data now:
select * from contacts
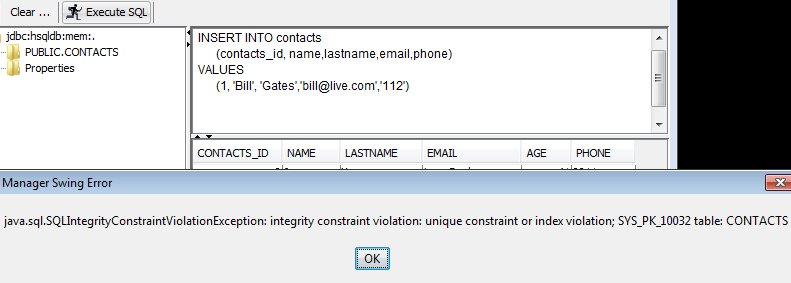
Let’s try to insert another data specifying the ID
INSERT INTO contacts
(contacts_id, name,lastname,email,phone)
VALUES
(1, 'Bill', 'Gates','bill@live.com','112')
We will get the following Error
This is because there is already a record ( Larry ) having the ID = 1 AND we did set the ID as primary key.
[info]In case you want to set a primary key, set to an INT with auto_increment. When inserting, try to specify it.[/info]
so, it is better changing the SQL command to:
INSERT INTO contacts
(name,lastname,email,phone)
VALUES
('Bill', 'Gates','bill@live.com','112')